Achilles tendinopathy is a common overuse injury that affects both athletes and non-athletes alike. As chiropractors, understanding the intricacies of this condition is crucial for providing effective, evidence-based care. This article explores the assessment and treatment of Achilles tendinopathy, offering insights into the latest research and best practices.
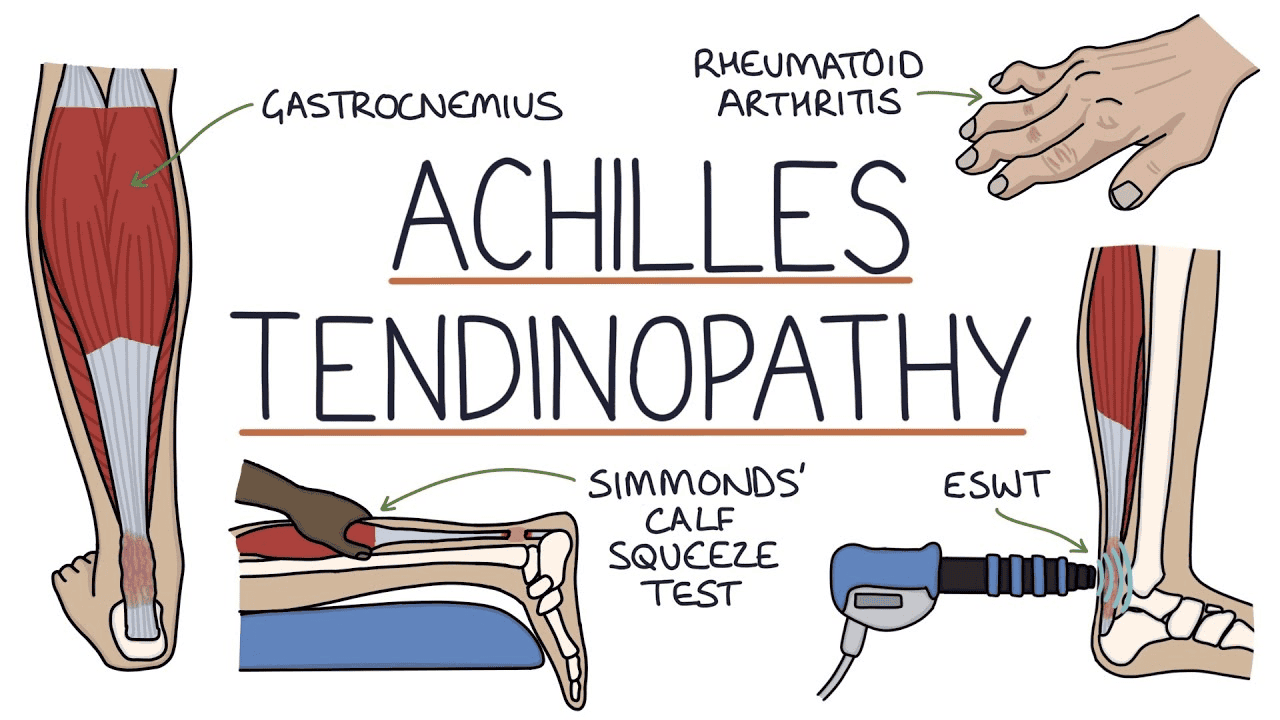
Achilles tendinopathy refers to a combination of pain, swelling, and impaired performance of the Achilles tendon. This condition can significantly impact a person’s mobility and quality of life. The Achilles tendon, the largest and strongest tendon in the human body, connects the calf muscles to the heel bone and plays a vital role in walking, running, and jumping activities.
Assessment of Achilles tendinopathy begins with a thorough clinical examination. Patients typically present with pain and stiffness along the Achilles tendon, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity. The pain often worsens with activity and may be accompanied by swelling and thickening of the tendon. Palpation of the affected area can help localize the pain and differentiate between insertional and non-insertional tendinopathy.
Functional tests are essential in the assessment process. The single-leg heel raise test is particularly useful, as it often elicits pain in patients with Achilles tendinopathy. The Thompson test, which involves squeezing the calf muscle to observe foot movement, can help rule out a complete tendon rupture. While clinical assessment is usually sufficient for diagnosis, imaging techniques such as ultrasound or MRI may be employed to confirm tendon thickening or identify structural damage in more complex cases.
When it comes to treatment, a multifaceted approach is key. Evidence-based strategies focus on promoting tendon healing and preventing recurrence. Eccentric exercise rehabilitation has shown significant efficacy in managing Achilles tendinopathy. This involves slowly lowering the heel from a raised position, which helps strengthen the tendon and improve its capacity to handle load.
Soft tissue mobilization techniques, including instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization (IASTM) and Active Release Technique (ART), can be beneficial in addressing adhesions and promoting blood flow to the affected area. These methods, when applied skillfully, can help reduce pain and improve tendon flexibility.
Addressing biomechanical factors is crucial in both treatment and prevention. This may involve assessing and correcting foot posture, gait analysis, and prescribing appropriate footwear or orthotics. Improving ankle range of motion and addressing any muscle imbalances in the lower extremity can also contribute to better outcomes.
While conservative management is the mainstay of treatment, it’s important to educate patients about the typically slow healing process of tendon injuries. Gradual return to activity, guided by pain levels and functional improvement, is essential to prevent re-injury.
In some cases, additional modalities such as low-level laser therapy or extracorporeal shockwave therapy may be considered, although the evidence for these treatments is mixed and they should be used judiciously.
As evidence-based chiropractors, it’s crucial to stay updated on the latest research and treatment protocols for Achilles tendinopathy. By employing a comprehensive approach that includes proper assessment, targeted exercises, manual therapy, and addressing biomechanical factors, we can effectively manage this condition and help patients return to their desired activities.
Remember, each patient’s presentation is unique, and treatment plans should be tailored accordingly. Regular reassessment and adjustment of the treatment approach based on patient progress is key to achieving optimal outcomes in managing Achilles tendinopathy.
By incorporating these evidence-based practices into your chiropractic care, you can offer patients effective, non-invasive treatment options for Achilles tendinopathy, promoting healing and improving long-term outcomes.

